Exploring the Sustainable Power of Hydropower Stations
Andrea Romagnoli October 27, 2023 0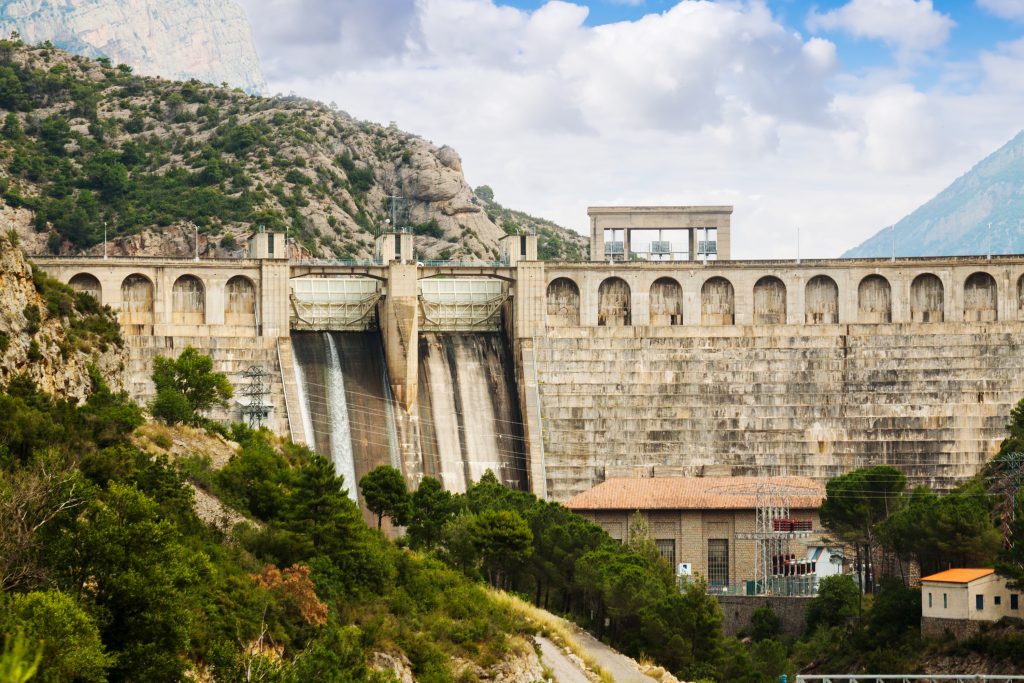
<a href="https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/hydro-electric-power-station-river_1329833.htm#query=hydropower&position=2&from_view=keyword&track=sph">Image by bearfotos</a> on Freepik
Hydropower: Tapping into the Power of Flowing Water for Electricity
Hydropower, also known as hydroelectric power, is a remarkable source of renewable energy that has been harnessed for centuries. It’s a technology that seamlessly integrates the power of flowing water to generate electricity. This article delves into the fascinating world of hydropower, exploring how it works, its environmental impact, its significance in the realm of clean energy, and its potential for a sustainable future.

The Mechanics of Hydropower
At its core, hydropower is a simple concept. It involves converting the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water into mechanical energy, which then turns generators to produce electricity. The essential components of a hydropower system include:
1. Dams: Dams create reservoirs where water is stored. The controlled release of water through turbines generates electricity.
2. Turbines: Turbines are the heart of hydropower systems. Water from the dam flows through these turbines, causing them to rotate.
3. Generators: Connected to the turbines, generators convert the mechanical energy from the turbines into electrical energy, creating the electricity we use.
4. Transmission Lines: The electricity generated is transmitted through power lines to homes and businesses.

Environmental Impact
Hydropower’s environmental impact largely depends on the scale of the project and its location:
1. Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Hydropower is a clean energy source, producing minimal greenhouse gas emissions during electricity generation.
2. Habitat Disruption: Large-scale hydropower projects can disrupt natural habitats, potentially affecting fish migration and ecosystems.
3. Water Management: The alteration of natural water flow can impact downstream areas, leading to water resource management challenges.
4. Reservoir Methane Emissions: Decomposing organic matter in reservoirs can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas. However, this is more prevalent in tropical regions.
Types of Hydropower Systems
Hydropower systems come in various forms, each with its unique features and applications:
1. Conventional Hydropower: This includes large-scale, reservoir-based projects with dams and extensive infrastructure. These systems often provide stable, base-load power.
2. Run-of-River Hydropower: Unlike conventional hydropower, run-of-river systems do not require large reservoirs or significant water storage. They allow for more natural river flow and are considered environmentally friendly.
3. Pumped Storage Hydropower: These systems operate like giant batteries. During periods of low energy demand, excess electricity is used to pump water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir. When demand is high, the water is released to generate electricity.
4. Tidal and Wave Energy: Tapping into the motion of ocean tides and waves, these systems are highly predictable and considered promising sources of clean energy.
Benefits of Hydropower
Hydropower offers a multitude of benefits:
1. Renewable and Reliable: It’s a consistent and renewable energy source, making it ideal for providing stable electricity.
2. Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Hydropower’s environmental footprint is smaller compared to fossil fuels.
3. Low Operating Costs: Once built, hydropower systems have low operating and maintenance costs.
4. Long Lifecycle: Properly maintained hydropower facilities can operate for decades.
5. Grid Stabilization: Hydropower contributes to grid stability and reliability by providing a constant source of electricity.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While hydropower holds significant potential, it faces challenges:
1. Environmental Concerns: Large-scale dams can disrupt ecosystems and require careful management.
2. Resource Availability: Not all regions have access to suitable water resources for hydropower.
3. Aging Infrastructure: Some existing hydropower facilities require upgrades or replacements to maintain efficiency.
4. Research and Innovation: Continued research is necessary to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of hydropower technology.
Hydropower’s ability to harness the energy of flowing water has been instrumental in providing clean electricity for decades. It stands as a vital player in the transition towards sustainable energy solutions. While environmental concerns and infrastructure challenges exist, the benefits of hydropower, such as reliability, low emissions, and long lifecycles, make it a key component in our pursuit of a cleaner, greener future. As technology evolves and we become more adept at balancing hydropower’s advantages with its environmental impact, we can tap into the incredible potential of flowing water to meet our growing energy needs. Hydropower is not just a part of our energy history; it’s a beacon guiding us towards a sustainable energy future.