Greenhouse gases
Greenhouse Gas and Environment
Greenhouse gases are gases that trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere.
They are essential for life on Earth, as they help to keep the planet warm. However, too many greenhouse gases can cause the Earth to warm too much, which can have a number of negative consequences for the environment.
Natural processes emit greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, but human activities are the primary cause of the increase in greenhouse gas levels over the past century. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is the largest source of human-caused greenhouse gas emissions. Other human activities that emit greenhouse gases include deforestation, agriculture, and industrial processes.
The Earth’s atmosphere has always contained greenhouse gases, but the levels of these gases have been rising since the Industrial Revolution. The increase in greenhouse gas levels is causing the planet to warm at an unprecedented rate. The average global temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit) since the late 19th century.
Carbon dioxide CO2 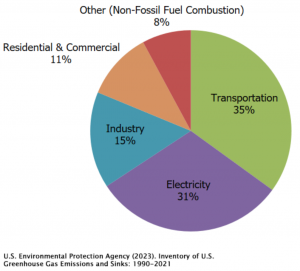 enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials, and also as a result of certain chemical reactions (e.g., cement production). CO2 is removed from the atmosphere (or “sequestered”) when it is absorbed by plants as part of the biological carbon cycle released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned.
enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials, and also as a result of certain chemical reactions (e.g., cement production). CO2 is removed from the atmosphere (or “sequestered”) when it is absorbed by plants as part of the biological carbon cycle released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned.
Methane CH4 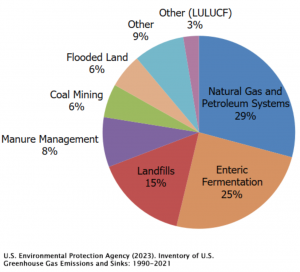 is emitted during the production and transport of coal, natural gas, and oil. Methane emissions also result from livestock and other agricultural practices, land use, and by the decay of organic waste in municipal solid waste landfills.
is emitted during the production and transport of coal, natural gas, and oil. Methane emissions also result from livestock and other agricultural practices, land use, and by the decay of organic waste in municipal solid waste landfills.
Nitrous oxide N2O is emitted during agricultural, land use, and industrial activities; combustion of fossil fuels and solid waste; as well as during treatment of wastewater.
Ozone: there are two types, good one and a bad one.
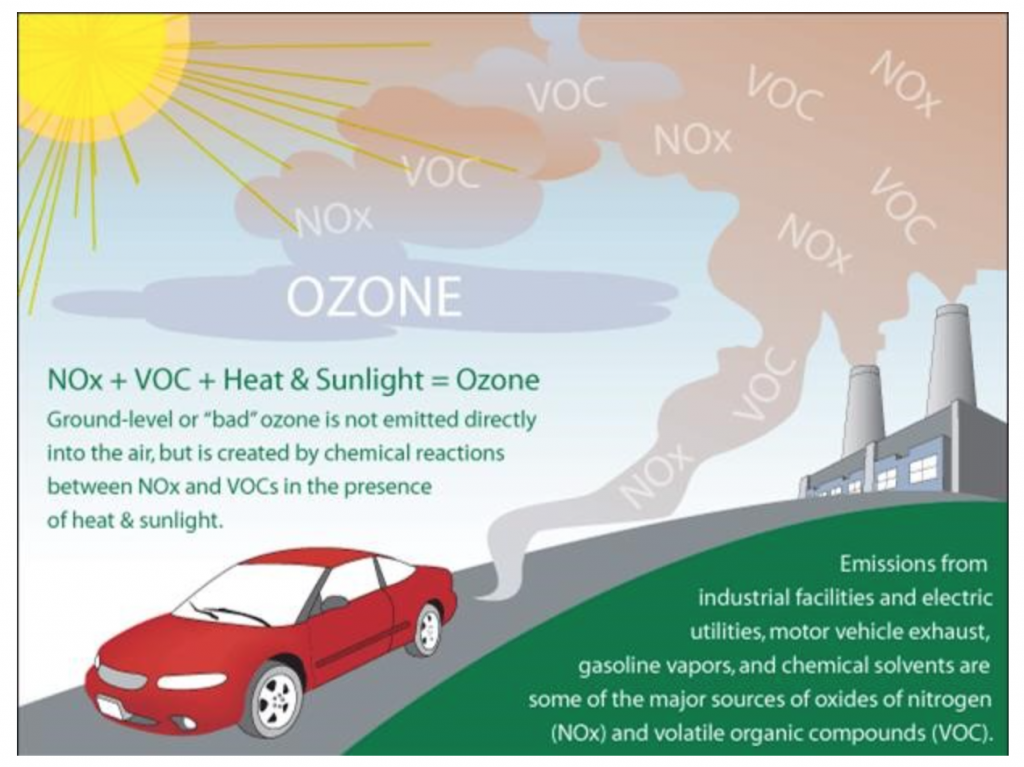
Stratospheric ozone is “good” because it protects living things from ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Tropospheric, ground-level ozone, topic of this article, is “bad” because can be harmful to animals and humans because it damages our lungs, sometimes making it difficult to breathe. It is created by chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOC).
This happens when pollutants emitted by cars, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, chemical plants, and other sources chemically react in the presence of sunlight. Ozone is most likely to reach unhealthy levels on hot sunny days in urban environments, but can still reach high levels during colder months. Ozone can also be transported long distances by wind, so even rural areas can experience high ozone levels.
Fluorinated gases: Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that are emitted from a variety of household (e.g. fridge, air conditioners), commercial, and industrial applications and processes. Fluorinated gases are typically emitted in smaller quantities than other greenhouse gases, but they are potent, they are sometimes referred to as high-GWP gases because, for a given amount of mass, they trap substantially more heat than CO2.
When greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, it causes the Earth’s temperature to rise. This is known as global warming.
Global warming can have a number of negative consequences for the environment, including:
- Rising sea levels: As the Earth’s temperature rises, the ice caps and glaciers melt, which causes sea levels to rise. This can inundate coastal areas and displace millions of people.
- More extreme weather events: Global warming can cause more extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts. These events can cause widespread damage to agriculture, disrupt transportation and infrastructure, displace people and loss of lives.
- Changes in plant and animal life: Global warming can cause changes in plant and animal life. Some species may be able to adapt to the changing climate, while others may not. This can lead to extinctions and loss of biodiversity.
- Freshwater scarcity: As the Earth’s climate warms, glaciers and ice sheets melt, which can reduce the amount of freshwater available for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
In addition to these environmental consequences, global warming can also have a number of negative consequences for human health. For example, it can increase the risk of heat-related illnesses, respiratory problems, and infectious diseases.
The good news is that there are things that can be done to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of global warming.

These include:
- Using renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power
- Improving energy efficiency in private homes and businesses
- Reducing deforestation and planting trees
- Driving less and walking, biking, or taking eco-friendly transportation more often.
- Businesses can also make changes, such as investing in renewable energy.
- Governments can play a role by enacting policies that promote clean energy and reduce emissions.
By taking these steps, we can help to protect the environment and ensure a sustainable future for our planet and for our kids and next generations to come.
The effects of greenhouse gases on the environment are already being felt around the world. If we do not take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the consequences may become more severe.